Next, on our look through the common specifications included with modern car audio amplifiers, we want to take a look at amplifier efficiency. With the electrical systems in modern cars shrinking in capacity with every passing year, getting power from your amplifier without taxing the wiring, battery, and alternator in your car is a genuine challenge and concern. Modern Class-D amplifiers have quickly become the standard to drive our speakers. Read on to find out why.
What Is an Amplifier Efficiency Specification?
The efficiency specification of the amp you have chosen will let you know how much of the electricity fed into your amp is converted to an audio signal and how much is wasted as heat. A typical specification would look like 75.1 percent at full power into a 4-ohm load. This information tells us that 75.1 percent of the power going into the amp is converted to audio and that 24.9 percent is used to process the audio signal and is converted to heat.
While comparing maximum power ratings is fun, the music we listen to is quite dynamic and its levels vary a great deal. We set up a pair of amplifiers in our lab and took a series of measurements to graph the efficiency of the amp relative to its power output capabilities.
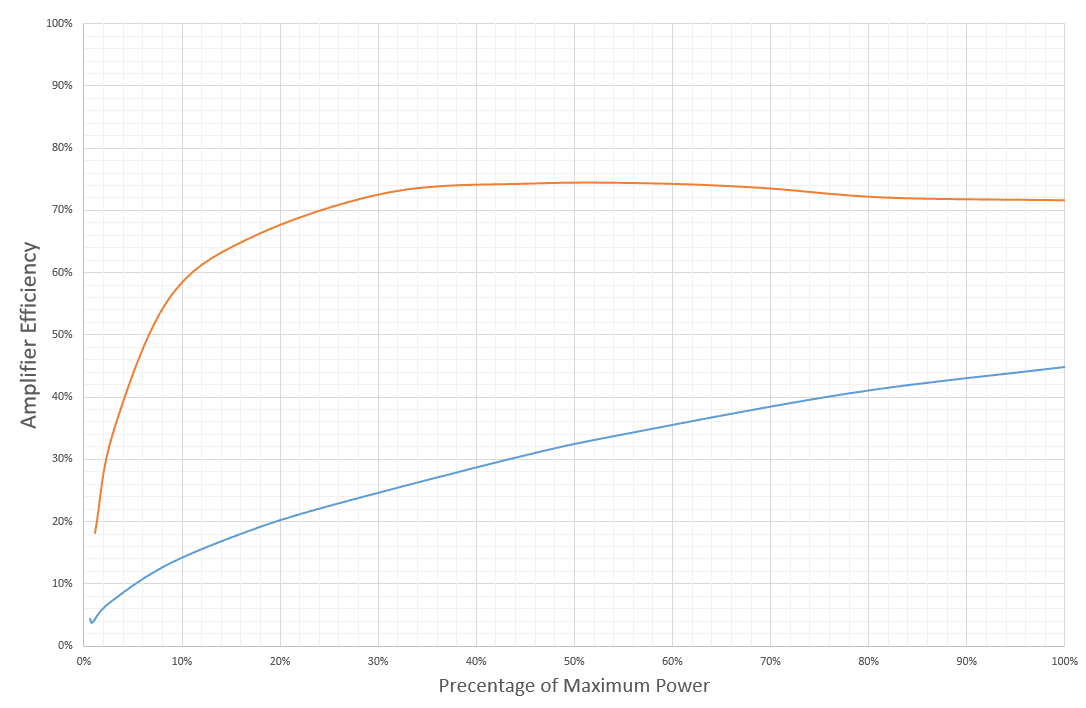
As you can see, the Class-D amplifier is, more often than not, at least twice as efficient as this particular (very low quality) Class-AB amp. Many reviewers list amplifier efficiency at two levels: full power and 1/3 of rated power. The two amps in this test delivered 23 percent and almost 71 percent efficiency at their 1/3 of maximum power rating. Indeed, you are reading that correctly. The Class-D amp would draw less than 33 percent of the current required to produce the same amount of power as the Class-AB amp. Since we operate our amplifiers in this range most of the time, even with the music quite loud, the effect on the vehicle’s electrical system can be dramatic.
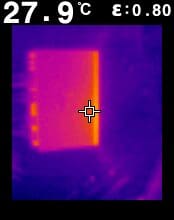
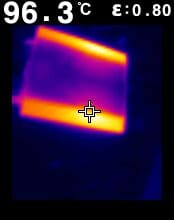
Where Does the Heat Go?
As mentioned, the energy that enters an amp that is not sent to the speakers is converted to heat. To illustrate this effect, we fired up these same two amplifiers and let them run at an output level of about 21 watts for 10 minutes. The thermal images below give you an idea of how they differ.
Where Efficiency Really Matters
In a motorcycle, UTV or side-by-side where the current production capabilities of the factory electrical system are quite limited, choosing an amp with excellent efficiency is significantly more important than, say, in a pickup truck that is equipped with a 180-amp alternator. For these applications, look for an amp that offers the highest efficiency number you can find. Several motorcycle-specific amplifier solutions exceed 90 percent efficiency at full power.
Idle Current Specification
Another specification you will see listed in reviews and some owner’s manuals is idle current. Idle current describes how much current the amplifier draws when it’s turned on but not playing any music. A relatively high or low number doesn’t necessarily mean the amplifier is worth avoiding or is better than another solution. For example, amplifiers with onboard microcontrollers or signal processors consume a little more current than an amp without these devices and subsequent features.
If you drive a vehicle with an adequate electrical system, then considering amplifier efficiency isn’t a huge concern. If you drive a compact to mid-sized car, a hybrid or any kind of type of powersports vehicle, keep an eye on those efficiency ratings. Your local mobile electronics retailer can help you choose a solution that will sound great.
