When it comes to subwoofer sizes for car audio systems, many people think that bigger is better. While we won’t argue with the fact that a speaker with more cone area can be more efficient, the output capabilities of a subwoofer depend significantly on the enclosure it’s installed in. In this article, we are going to look at a sure-fire way to make sure you get the bass performance you want from your mobile audio system.
Why Do You Need a Car Audio Subwoofer?
Making good bass that is clear and loud requires a lot of air movement. A small 4-inch speaker in the dash of your car or truck simply can’t move far enough to pressurize and rarify enough air to make acceptable bass. Subwoofers are speakers that are designed to play frequencies below 100 Hz. These speakers feature large voice coils to dissipate large amounts of heat, with suspension designs that allow for lots of cone movement. When installed in a properly designed enclosure, subwoofers relieve the smaller speakers from having to try to play bass frequencies. Being able to focus on midrange information reduces cone excursion requirements and decreases distortion.
Subwoofer Size Versus Low-Frequency Extension
When buying a subwoofer, you need to determine how much space you’re willing to assign for the enclosure. Larger subwoofers require a larger enclosure to produce the same amount of low-frequency output as smaller-diameter subwoofers. To begin to understand this concept, let’s use a few examples. Say we have enough room to have an enclosure built with an internal air volume of 2 cubic feet. This is a very flexible size in that the options for subwoofer are extensive. We could use a pair of tens with the enclosure sealed, a pair of tens with a vented design, a pair of twelves sealed, or a single 12 in a vented design. Which is loudest? Which is best? Let’s have a look.
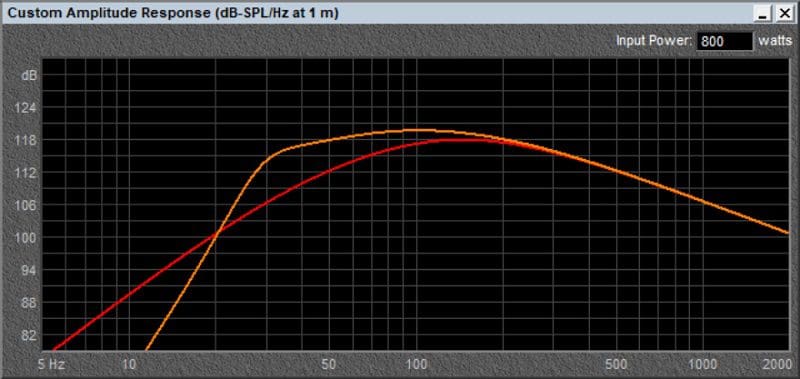
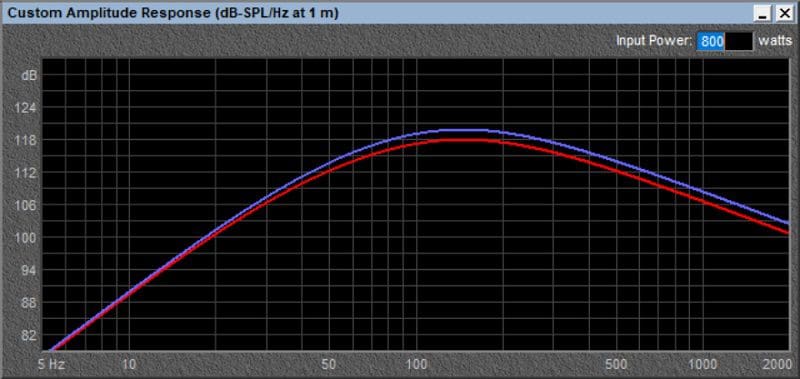
The graph below shows the predicted free-field output of a pair of ARC Audio Black Series 10-inch V2 subwoofers in a sealed and vented design with a total volume of about 2 cubic feet. The red curve is the sealed design and the orange curve is the vented design.
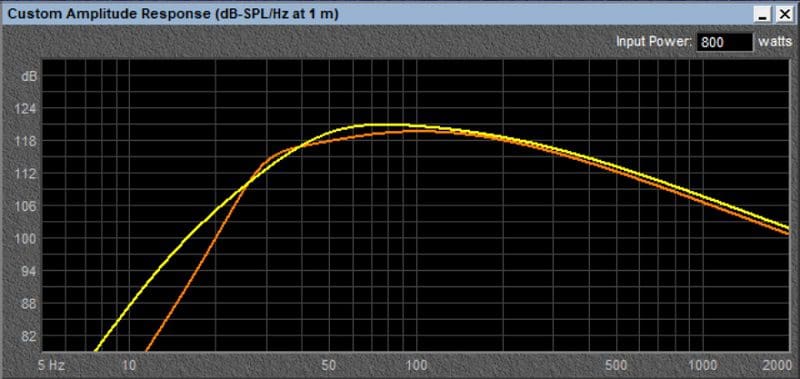
The vented design increases the total system efficiency at all frequencies from 20 Hz to beyond 100 Hz. In this simulation, the dual 10-inch vented design is the winner. What about using larger woofers? Let’s compare the performance of a pair of Black 10’s to a pair of Black 12 subwoofers. The yellow line in the graph below represents the predicted output of a pair of Black 12V2 subs.
As you can see, in this simulation, the response curve of the 12-inch subwoofers mimics that of the tens, but with an increase in efficiency of more than 3 dB.
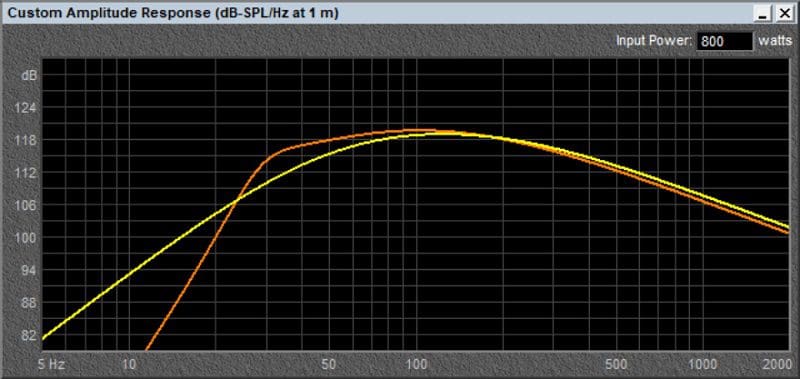
Here’s where things start to get tricky. What about a pair of tens in a vented design as compared with a pair of twelves in a sealed enclosure? The graph below tells the tale.
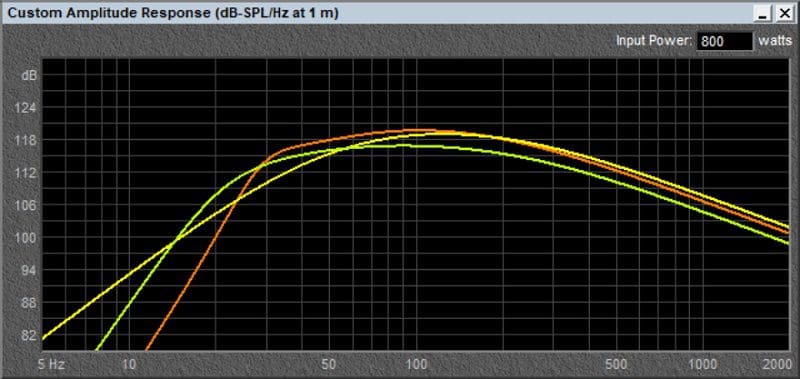
Down to 25 Hz, the tens in the vented design are more efficient than the twelves in a sealed design. What if you want good efficiency and want to fill in that deficiency in efficiency below 25 Hz? How about throwing a simulation of a single twelve into the mix?
The green line added to the previous graph shows the response of a single ARC Audio Black 12V2 subwoofer in a 2-cubic-foot vented enclosure. It’s not as loud as the pair of tens or twelves above 30 Hz, but it’s the loudest at 20 Hz. It all depends on your choice of music and how much low-frequency extension you’re after.
More Subs Isn’t Always Better
We are going to add one more graph to our article. This graph shows the original pair of 10-inch Black-series subwoofers in the 2-cubic-foot sealed enclosure in red and the predicted response of using three of those subs in the same enclosure. Up at 70 or 80 Hz, there is some increase in output, but down around 30 or 40 Hz, where the fun bass exists in most music, the output is almost the same. So, is there an advantage to running three subwoofers in this enclosure? Not really.
What About Subwoofer Power Handling?
The final consideration in this discussion of the best subwoofer choice for a given amount of space is power handling. There are two types of power handling to take into consideration with subwoofers: thermal and physical. Thermal power handling is determined primarily by the size of the subwoofer voice coil. Larger coils can handle more heat. In the case of the Black subwoofers in this article, both subs have a 3-inch coil, but the 12 has a 500-watt RMS power rating as opposed to the 400-watt rating of the 10.
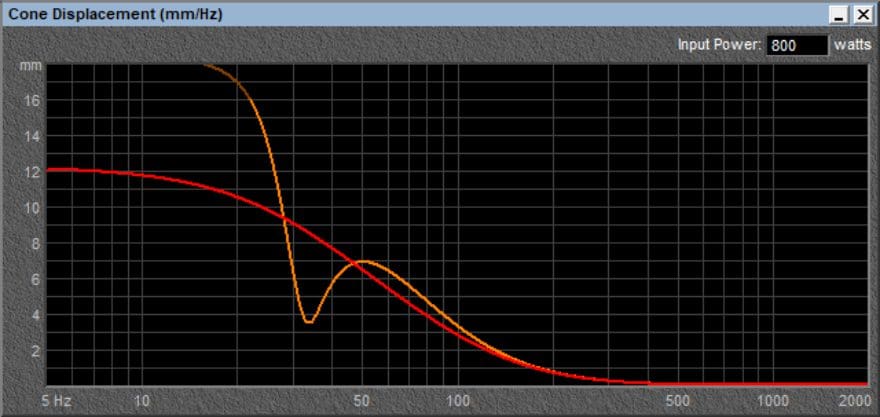
In terms of physical power handling, that’s something that needs to be evaluated in simulation software. The graph below shows how far the woofer cones move relative to frequency. The chart below shows the sealed tens in red and the vented tens in orange. With an Xmax spec of 16 mm, the vented enclosure is good to just around 22 Hz. At that point, the cone might bottom out. Adding an infrasonic filter at this frequency would help prevent damage. In reality, unless you’re deliberately playing music with lots of extremely deep bass, you should be fine.
Upgrade Your Car Stereo with a Subwoofer
If you’re heading to your local specialty mobile enhancement retailer to talk about adding a subwoofer to your audio system, start by planning how much space you can allot to the enclosure. This information will help the product specialist determine what size subwoofer and how many are best for your listening preferences.